Academician bian xiuwu's team develops new mof-based nanomedicine to enhance the effect of radiotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer
radiotherapy (rt) is one of the important clinical treatments for local control of triple-negative breast cancer (tnbc), but radioresistance still limits the therapeutic effect of this strategy. in view of this, the team of academician bian xiuwu, professor yang yi and professor tian gan from southwest hospital of army medical university and jinfeng laboratory designed an atp/ph dual-responsive release mof-based nanomedicine using a dual radiosensitization method, which can effectively deliver iron ions and inhibiting glutathione (gsh) synthesis to synergistically induce ferroptosis, combined with the radiotherapy sensitizing effect of high atomic number nanomaterials, jointly promotes the radiotherapy effect of tnbc. the research was published in acs nano in the form of a paper titled "a mof-based potent ferroptosis inducer for enhanced radiotherapy of triple negative breast cancer."

the nanomaterial synthesis process is shown in figure 1. first, l-butyrine-sulfoximine (bso) was loaded into zif-8 through a one-step method, and then gold nanoparticles (au nps) were grown on its surface. using bso/zif-8@au as a template, an iron-based metal polyphenol (mpn) network structure was grown, and finally modified with hyaluronic acid (ha) to obtain the final nanomaterial bso/zif-8@au@mpn@ha (bzamh). bso can inhibit γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (γ-gcs) and reduce intracellular gsh biosynthesis, thereby indirectly inactivating gpx4. fe2+ released from mpn can generate hydroxyl radicals (•oh) through the fenton effect. inactivation of gpx4 and local generation of •oh together induce potent ferroptosis. modified au nps can improve the energy deposition of incident x-rays. each component synergistically promotes ferroptosis and enhances rt to effectively treat tnbc while inhibiting tnbc lung metastasis (figure 1b).
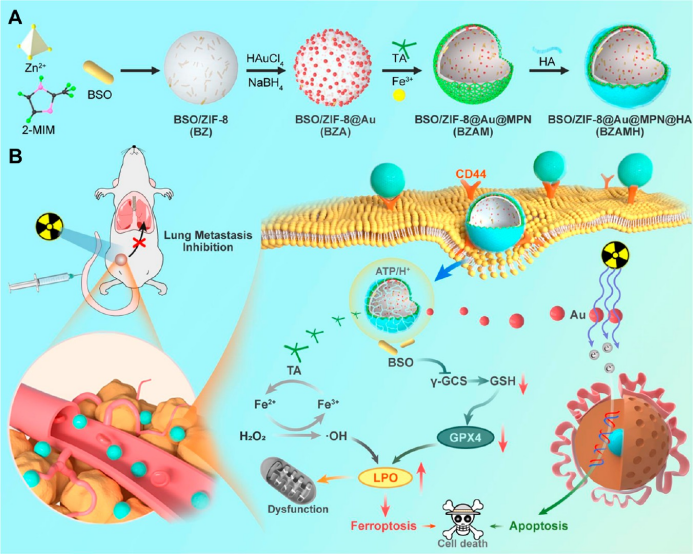
▲figure 1. synthetic route and action mechanism diagram of mofs-based ferroptosis nano-inducer
[characterization of physical and chemical properties of bzamh nps]
the prepared bzamh nps exhibit a hollow spherical structure, and the hydrated particle size is approximately 200 nm. after the mpn shell is grown, the bzamh nps are transformed into an amorphous hollow structure due to the etching and reduction of ta, and the iron ions on the surface are mostly fe2+, which provides favorable conditions for the subsequent fenton reaction.
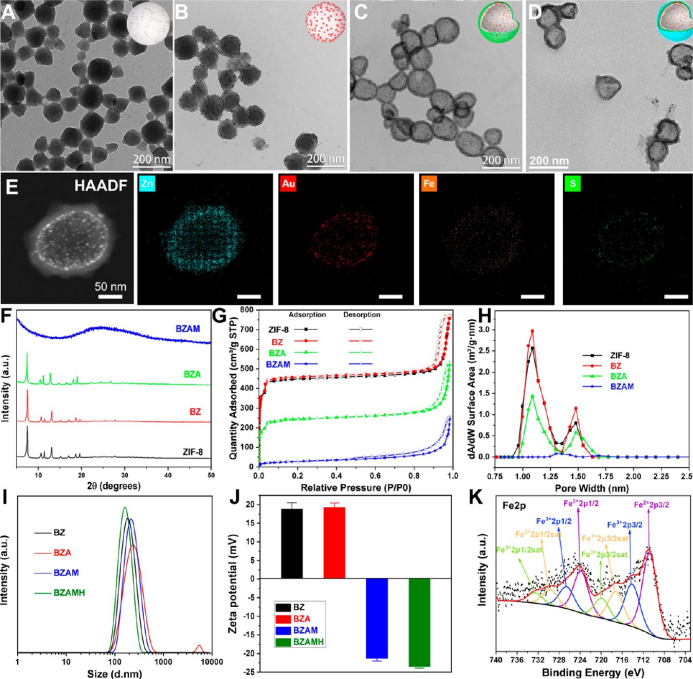
▲figure 2. characterization of physical and chemical properties of bzamh nps
[bzamh nps can effectively induce ferroptosis]
bzamh nps deplete cellular gsh and amplify oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis. using 4t1 mouse cells as a model, the experiment demonstrated that bzamh nps can be effectively endocytosed by cells, and can successfully consume intracellular gsh, downregulate gpx4 expression, cause the accumulation of lipid peroxide (lpo), and thus induce significant iron death effect.
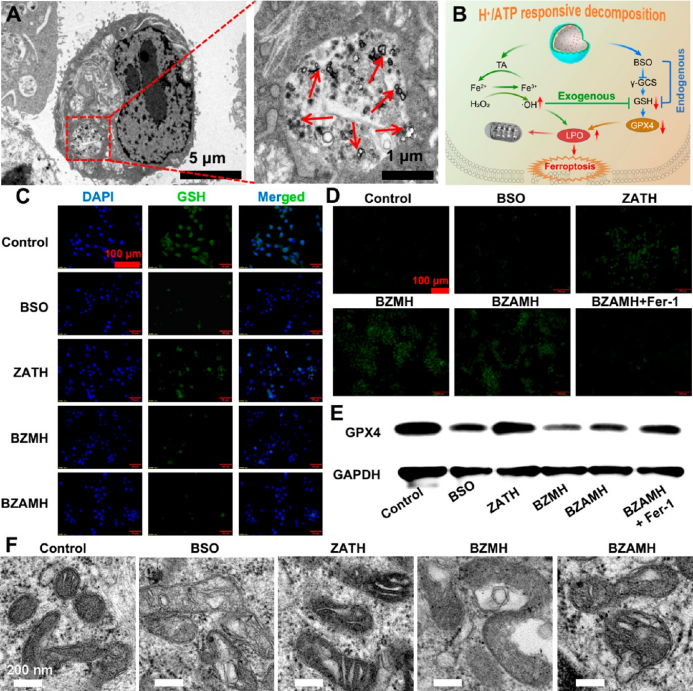
▲figure 3. bzamh nps can effectively induce ferroptosis
[feroptosis can synergistically enhance rt with au nps]
ferroptosis enhances rt and synergizes with au-mediated radiosensitization. experiments have proven that both ferroptosis and au nps can significantly promote the inhibitory effect of rt on tumor cells. bzamh nps can synergize the two effects, causing more obvious dna damage and showing the strongest cell growth inhibitory effect.
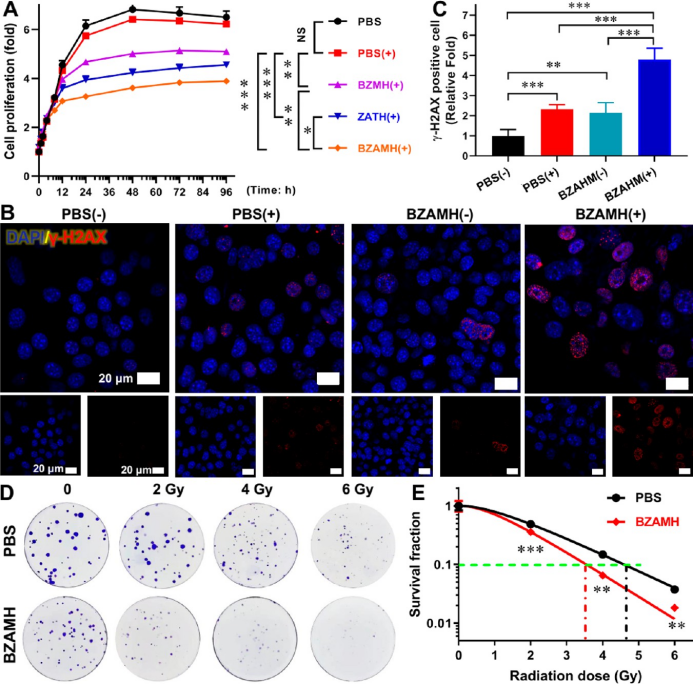
▲figure 4. ferroptosis can synergistically enhance rt with au nps
【in vivo anti-tumor experiment】
bzamh nps exhibit significant tumor growth inhibition in vivo. based on the results of in vitro treatment, we further studied the anti-tumor effect of bzamh nps in vivo. experiments show that bzamh+x-ray-mediated ferroptosis and rt have the most obvious tumor growth inhibition effect and extend the survival period of mice. staining of tumor tissue sections revealed that bzamh+x-ray can significantly reduce the expression of ki67 and gpx4, causing severe dna damage, thereby successfully inhibiting cell proliferation and tumor growth.
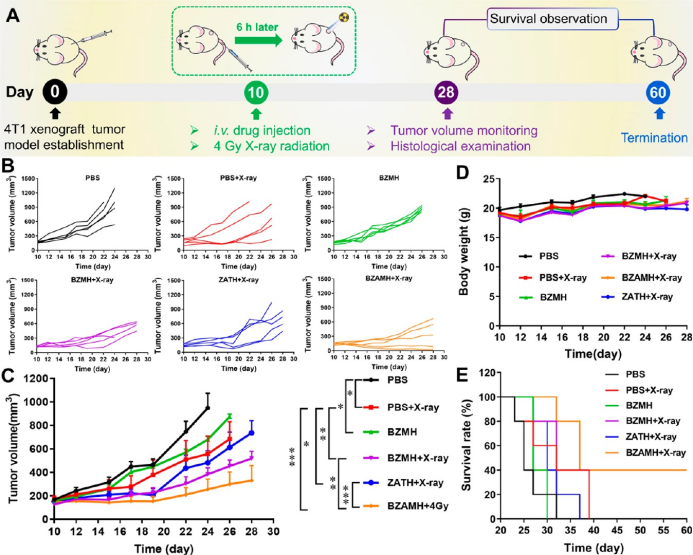
▲figure 5. in vivo anti-tumor experiment of bzamh nps
[research on anti-pulmonary metastasis]
the anti-metastasis ability of bzamh nps was studied using dual models of blood flow metastasis and breast cancer in situ lung metastasis. a blood flow model study found that bzamh + reduce the occurrence of breast cancer lung metastasis.
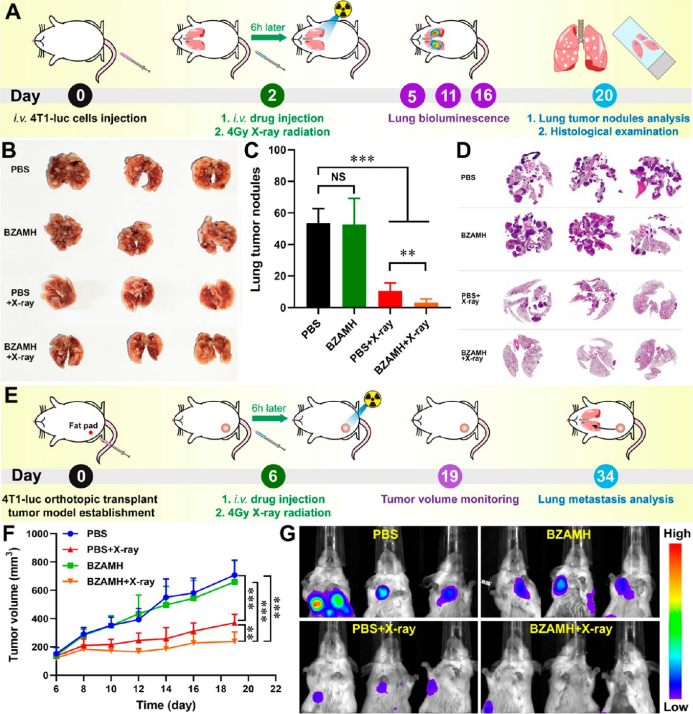
▲figure 6. anti-pulmonary metastasis study
【summary】
this study developed a mofs-based nanomedicine that can controllably deliver ferrous ions to trigger the fenton-like effect to perform ferroptosis, and can inhibit gsh production to inactivate gpx4 to destroy the ferroptosis defense system. the two synergistically induce strong ferroptosis. iron death. combined with the radiotherapy sensitizing effect of au nps, it can effectively inhibit tumor growth and show stronger anti-breast cancer lung metastasis efficacy. in summary, the smart nanomedicines introduced in this study provide new insights into anti-cancer treatment and are expected to provide a reliable reference for the development of the next generation of nanomedicines.
- About Us
-
Research Platform
- Major Disease Sample Database
- Innovative Drug Verification And Transformation Platform
- Experimental Animal Center
- Life And Health Future Laboratory
- Biomedical Imaging Platform
- Cell Multi-Omics Platform
- Pathology Technology Platform
- Bioinformatics Research And Application Center
- Jinfeng Pathology Precision Diagnosis Center
- Research Team
- Information Center
- Join Us


 渝公网安备50009802002274
渝公网安备50009802002274